Bimagrumab is a promising option for the treatment of obesity, significantly reducing total body fat mass in clinical studies. Unlike most other approaches to treating obesity, bimagrumab acts directly on fat cells without reducing appetite and without prompting lean mass loss.
U.S. Obesity Prevalence
Obesity prevalence has roughly tripled since 1975. More than 40% of adults in the United States currently live with obesity—a figure predicted to rise to 50% by 2030. Obesity is a leading risk factor for the development of many serious health conditions, including cardiometabolic disease and heart failure.
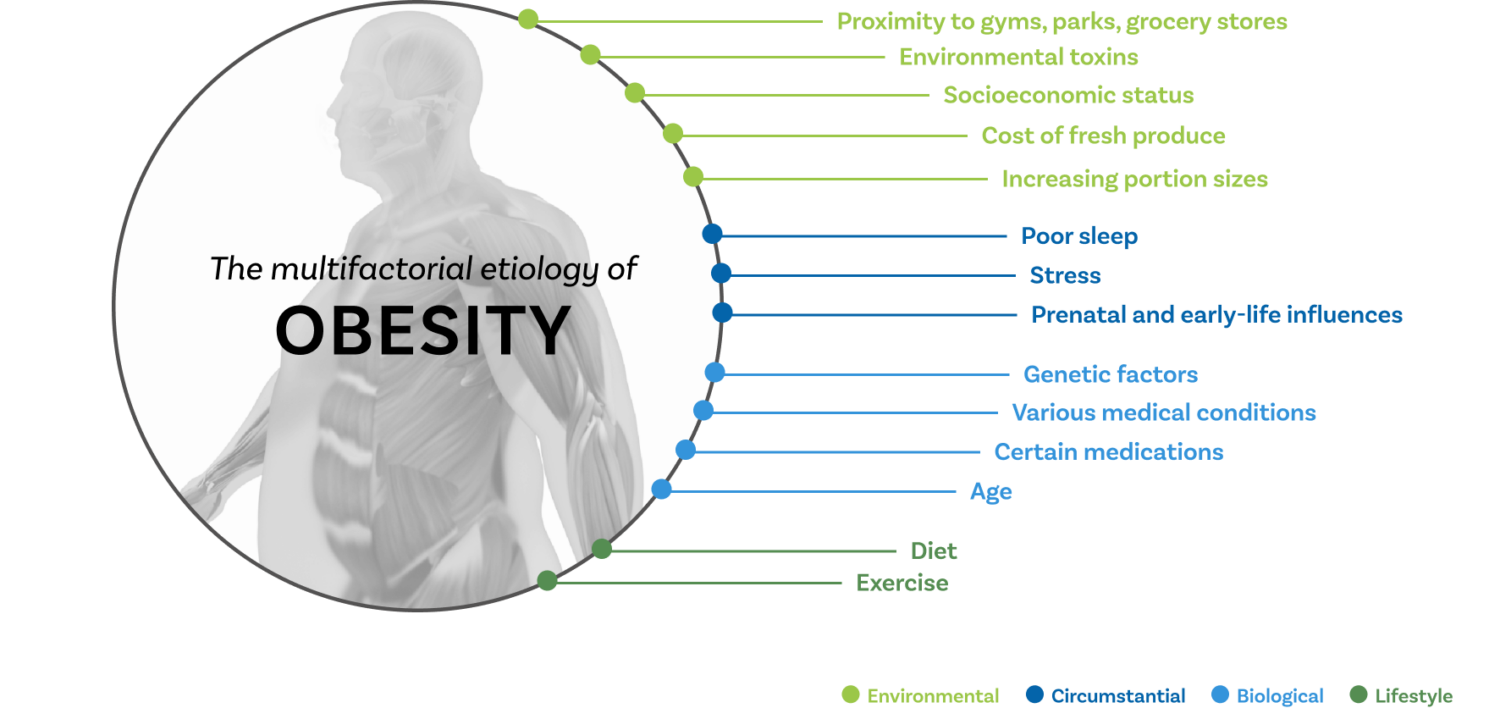
A complex disease with multifactorial etiology
Obesity is increasingly recognized by researchers and healthcare providers as a complex disease caused by a combination of environmental and biological factors. New interventions are needed to help address the full scope of the disease drivers.
Limitations and tradeoffs of current obesity interventions

Diet & Exercise
A critical recommendation central to any weight management treatment
- Puts onus solely on patient’s ability to follow diet and exercise plan
- Metabolic adaptations counteract weight loss
- Does not address underlying causes of the disease

Surgery
An effective but invasive option for people with Class III obesity
- High incidence of persistent gastrointestinal problems following procedures
- Invasive procedure
- Requires major lifestyle changes in diet and portions

Pharmaceuticals
Recent therapies are a welcome addition to the treatment landscape, yet challenges remain
- Tolerability issues, including abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting
- Substantial loss of lean mass in addition to fat mass

